 Table of Contents
Table of Contents  Previous Section
Previous Section
Flattened Relationships
In addition to flattening attributes, you can also flatten relationships. Flattening a relationship gives a source entity access to relationships that a destination entity has with other entities. It's equivalent to performing a multi-table join. Note that flattening either an attribute or a relationship can result in degraded performance when the destination objects are accessed, since traversing multiple tables makes fetches slower. When Should You Use Flattened Relationships?
As discussed in When Should You Use Flattened Attributes?, flattening is a technique you should only use under certain conditions. Instead of flattening an attribute or a relationship, you can instead directly traverse the object graph, either programmatically or by using key paths. This ensures that your application has an internally consistent view of the data.
There is one scenario in which you might want to use a flattened relationship: if you're modeling a many-to-many relationship and you want to perform a multi-table hop to access a table that lies on the other side of an intermediate table. For example, in the Movie database, the Director table acts as an intermediate table between Movie and Talent. It's highly unlikely that you would ever need to fetch instances of Director into your application. In this situation, it makes sense to specify a relationship between Movie and Director, and flatten that relationship to give Movie access to the Talent table.
Flattening a Relationship
To flatten a relationship:
- Add a relationship from one entity (entity_1) to a second entity (entity_2).
- Add a relationship from entity_2 to a third entity (entity_3).
- From entity_1, select the relationship to entity_2 to display its properties.
- In the list of properties for entity_2, select the relationship (talent) you want to flatten.
- Choose Property
 Flatten Property.
Flatten Property.
For example, you can add a to-many relationship called toDirectors from Movie to Director since a movie can have more than one director.
For example, you can add a to-one relationship called talent from Director to Talent. For each director a movie has, there is a corresponding single entry in the Talent table.
From Movie, select the relationship toDirectors to display the properties of Director.
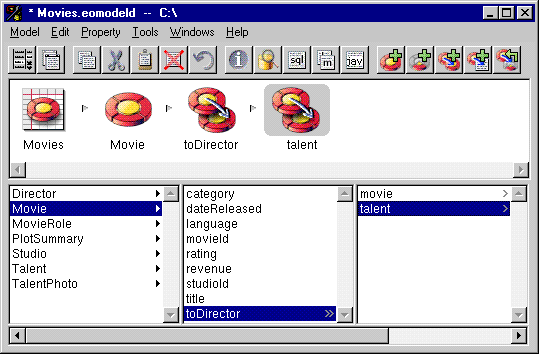
Figure 33. Flattening a Relationship
 Table of Contents
Table of Contents  Next Section
Next Section