Legacy Document
Important: The information in this document is obsolete and should not be used for new development.
Important: The information in this document is obsolete and should not be used for new development.
-
You can use the-symbol to subtract one real number from another.
x - y
x- Any floating-point number.
y- Any floating-point number.
DESCRIPTION
The-operator performs the standard subtraction of two floating-point numbers.EXCEPTIONS
When x and y are both finite and nonzero, either the result of x - y is exact or it raises one of the following exceptions:
- inexact (if the result must be rounded or if an overflow or underflow occurs)
- overflow (if the result is outside the range of the data type)
- underflow (if the result is inexact and must be represented as a denormalized number or 0)
SPECIAL CASES
Table 6-4 shows the results when one of the operands of the subtraction operation is a zero, a NaN, or an Infinity. In this table, x is any floating-point number.
Table 6-4 Special cases for floating-point subtraction Operation Result Exceptions raised x None -x None +0 None x None -x None None +0 None x - NaN NaN None[6] NaN - x NaN None[6] None + 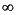
None NaN Invalid + 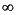
None None NaN Invalid
[6] If the NaN is a signaling NaN, the invalid exception is raised.