-
Streaming Audio on watchOS 6
Streaming audio on Apple Watch allows customers to enjoy your content wherever they go without their iPhone. Learn about the streaming APIs brought over from iOS to allow watchOS apps to create independent audio consumption experiences. Find out how to set up your audio session for streaming and explore best practices to provide the best experience for people moving between different network conditions.
리소스
관련 비디오
WWDC21
WWDC20
WWDC19
-
비디오 검색…
Last year in watchOS 5, we introduced the ability to play local, long-form audio in the background.
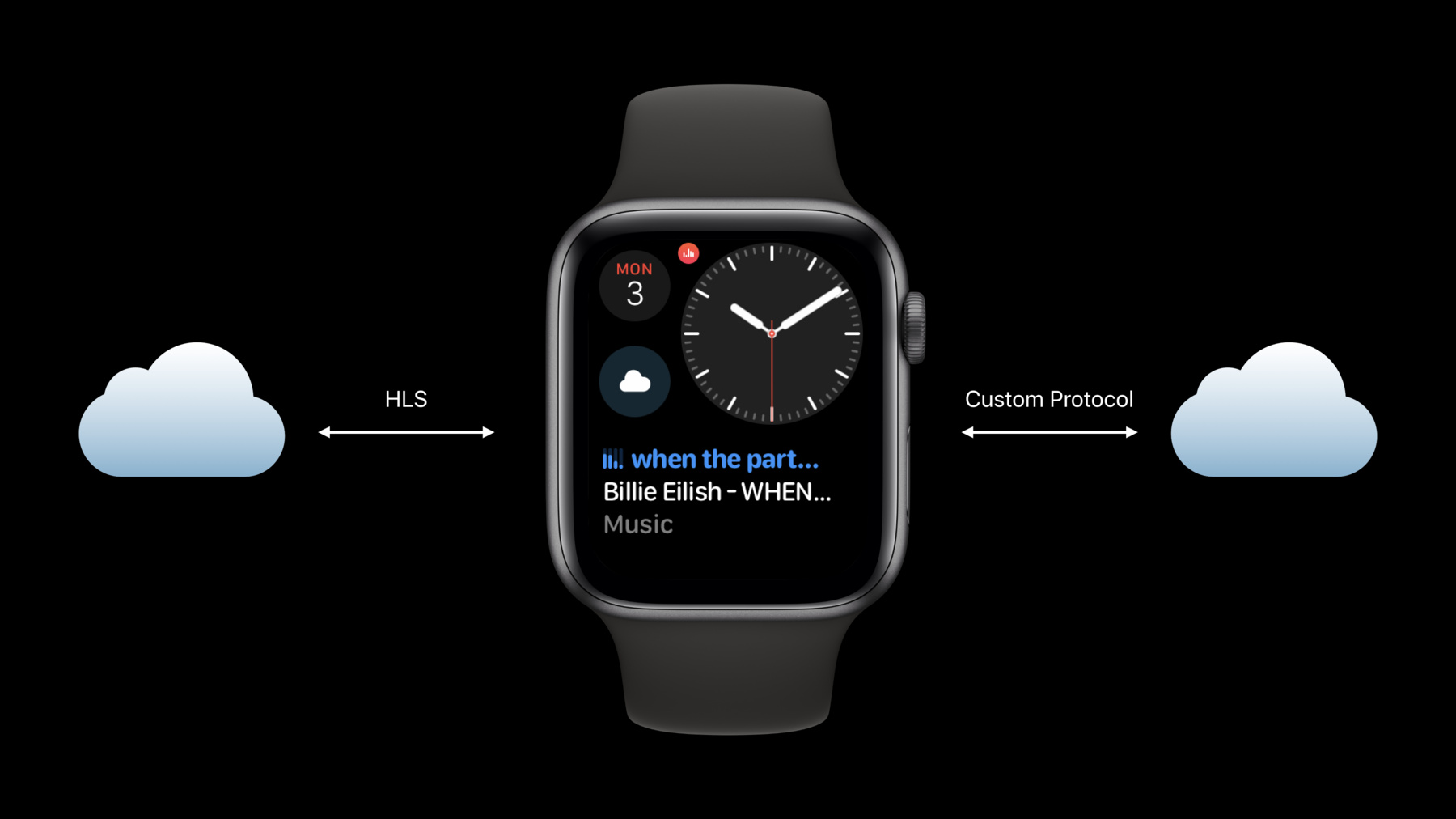
This year with watchOS 6, we're bringing the ability for watch apps to stream audio directly on Apple Watch.
This means that your customers no longer need to bring their iPhone with them to access your audio content, they no longer need to sync audio content to their watches, and they now have access to live audio programing like sports events.
WatchOS 6 supports two main ways to stream audio to Apple Watch. HLS and custom audio protocols. Let's dive into a bit more detail. If your content is available as an HLS audio feed, you can point AVQueuePlayer to the feed and it will take care of streaming your content.
WatchOS is optimized for HLS audio feeds and makes it simple to get started with.
Applications that use proprietary audio formats or use custom protocols are a bit different.
They need to use URLSession on the network framework to retrieve and interpret their metadata and audio content.
Once audio content has been downloaded to the watch, use AVFoundation for audio route selection and audio playback.
Audio streaming is made possible in watchOS 6 by bringing several iOS APIs into the watchOS SDK. Our goal has been to bring the two SDKs closer together so that your code can run watchOS with little or no modification.
For networking, watchOS 6 now has the network framework, first introducing iOS 12. This framework provides a modern alternative to unit sockets. Network framework is not only more on C API but also provides a very convenient Swift API. URLSession brings URLSessionStreamingTask to watchOS. It also brings along URLSessionWebSocketTask, which is new in both iOS 13 and in watchOS 6.
Audio streaming presents special challenges to the way the data is retrieved from the network. To this end, URLSession has added the new AV streaming network service type. You should use it for your streaming data request.
For audio playback, AVFoundation is bringing many of their APIs to watchOS 6 including AVPlayer and AVQueuePlayer.
Also, for the first time, CoreMedia is available in watchOS.
If your application is already set up for background audio playback, it is ready for audio streaming. No other project configuration is needed.
If your project is not configured for background audio, you will need to add this capability to the WatchKit extension target. For this, open your Xcode project and go to your WatchKit extension target settings.
On the signing and capability section, click Add Capability and select Background Modes.
Finally, under Background Modes, select the Audio Mode. This is all that needs to be done. Now that the project is configured, let's talk about the different APIs that need to be used during audio playback. After your app launches and before you activate an audio session, you may need to retrieve data from your servers.
This data is needed to present streaming options and content to users. For example, album information, playlist information, all metadata about the content of your applicant stream.
You may have already cached this data when your app activated or during the background refresh opportunity. If not, use URLSession to retrieve your data. At this time, socket, streaming task, and the network framework will not be available for use.
Once you have all the information you need to begin streaming, activate an audio session. The audio session should not be activated before this point, because activating one can disrupt the user experience. This is a very important difference between watchOS and iOS. On iOS, there's always a default audio route available. Let's figure out. This is not the case for watchOS.
When you activate an audio session, watchOS will automatically present an audio route picker on behalf of your application if no route is currently active.
There are two cases where watchOS may be able to skip presenting the audio route picker. For any Bluetooth device, if the device is already connected to the watch, or for Bluetooth devices based on the Apple wireless chip set, if the device is connected to the iPhone, the watch may temporarily borrow it. There are cases where this is not possible though, for instance, if you are on a phone call while connected to your iPhone. Once your application has an active audio session, all of the networking APIs are available to retrieve audio content. This includes URLSessionStreamingTask, URLSessionWebSocketTask, and the network framework.
If you attempt to use these APIs without an active audio session, your calls will fail.
Finally, your application has reached the point where it has enough audio data to start playback. You can now use AVFoundation to play your audio content. If you need to request new information from your servers to do your streaming, you can use all available networking APIs to do this. Now, let's talk about some audio streaming best practices for Apple Watch.
Audio streaming on Apple Watch is available in Series 3 and later.
This means that your application needs to check if audio streaming is available on the watch it is running on. In watchOS 6, use WKInterphaseDevices supportsAudioStreaming to make this check.
The additional audio and networking APIs in watchOS 6 mean that applications no longer need to use WatchKit's WK audio file APIs. For this reason, these APIs have been deprecated starting with watchOS 6.
Now, let's discuss some networking best practices.
Caching is very important. The right amount of audio data should be locally available at all times to cope with changing network conditions.
The number of network requests and their sizes should be reduced to the absolute minimum. Extra requests that did not post a problem on other devices may delay or stall playback. The same is true for downloading unnecessary data in those requests. All of these can result in poor user experiences.
To be safe, start streaming using 64 kbps encoded audio data. Monitor the speed at which data arrives to your application and only upgrade to higher bit rates if the network conditions allow for them. AVFoundation automatically does this for HLS audio streaming.
Do not rely on network reachability. Due to the nature of networks, the information returned by this API may no longer be valid by the time your application uses it. For the best user experience, always assume that you have a network connection and gracefully handle stalls and failures, and always adjust in real-time the audio quality and the amount of caching that your application does. Finally, your application is likely to experience more network transitions when running an Apple Watch. As the watch moves away from the iPhone, a good transition from Bluetooth to Wi-Fi or cellular. It is not uncommon for the watch to go between these three network types while your app is running. Your application should be prepared for such transitions, which can take several seconds to complete. As you can see, when bringing audio streaming applications to Apple Watch from other platforms, Apple or otherwise, you should be prepared for the possibility that you will need to optimize your networking code and protocols. If you need more information to get started writing audio applications for Apple Watch, Creating Audio Apps for watchOS is a great start. The information in the network framework introduction talk is 100% applicable to watchOS. Finally, check out these other sessions to help create a great audio streaming experience.
-